Bluetooth in Dual-Boot System
Problem Description
In a dual-boot system with Windows and Linux (Ubuntu), the same Bluetooth device (e.g., mouse, keyboard, headset, etc.) cannot automatically connect to PC when switching from one OS to another.
Analysis
Each hardware device has a unique MAC address that is used for identification and communication. When a Bluetooth device connects to an OS, the OS stores the MAC address and encryption keys for that device. After switching to another OS, the new OS does not have the corresponding encryption keys stored, making it impossible for the Bluetooth device to connect automatically.
Solution
To resolve this issue, two OSes need to share the same Bluetooth device information, including MAC addresses and encryption keys. This can be achieved by manually copying the Bluetooth configuration parameters from one OS to another.
Steps to Share Bluetooth Configuration Between Windows and Ubuntu
Case: Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) devices
1. Pair the Bluetooth device with Ubuntu first. Then switch to Windows and pair the same device there.
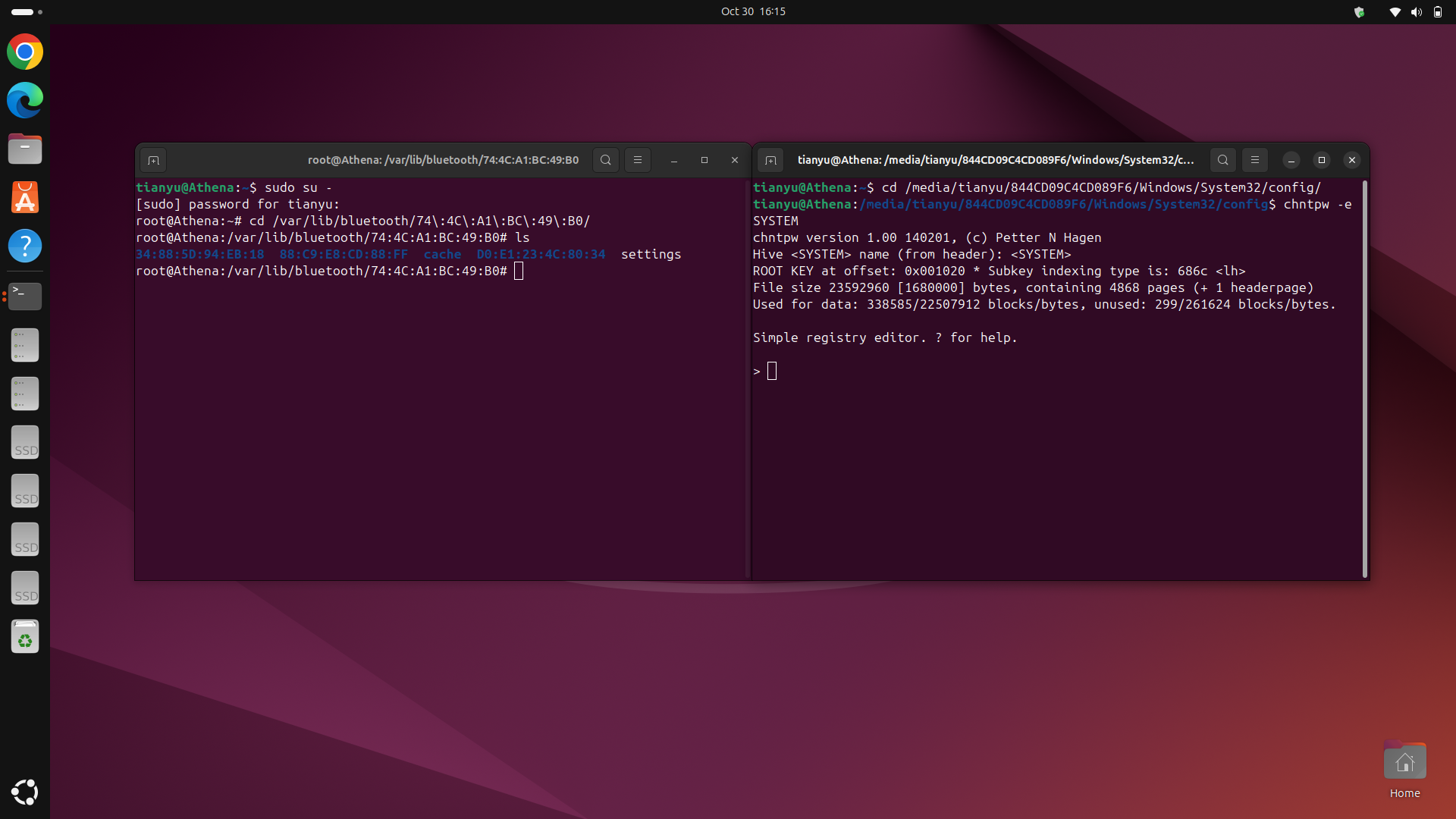
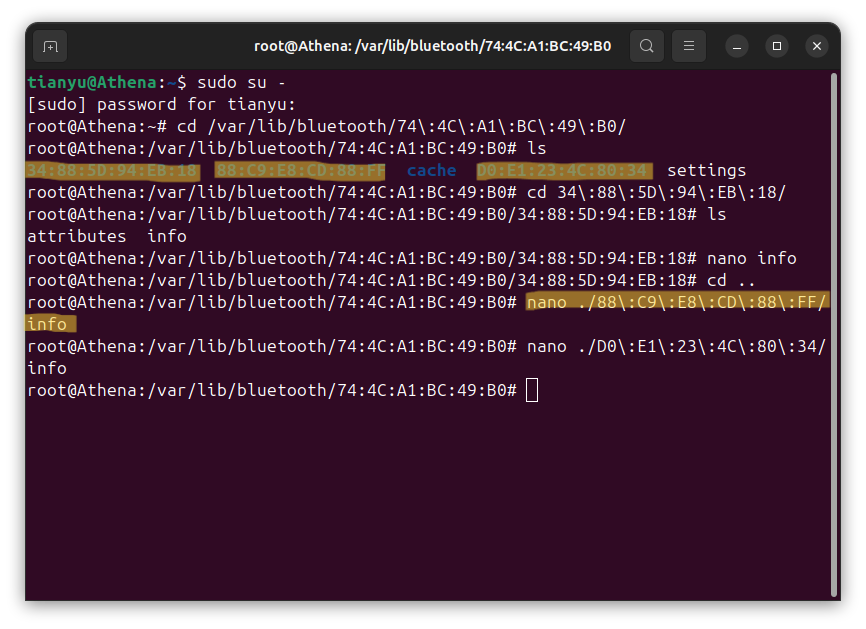
2. Go back to Ubuntu and open two terminal windows.
3. In the first terminal, navigate to the Bluetooth configuration directory for Ubuntu:
sudo su -
cd /var/lib/bluetooth/<your-ubuntu-bluetooth-controller-mac-address>/<your-device-mac-address>/
nano info
Attention: Must check the <your-device-mac-address> folder name, it should be the same as the device MAC address you paired in Windows. If not, use command mv <old-name> <new-name> to rename it. (Check step 4 for Windows to find out the correct device MAC address.)
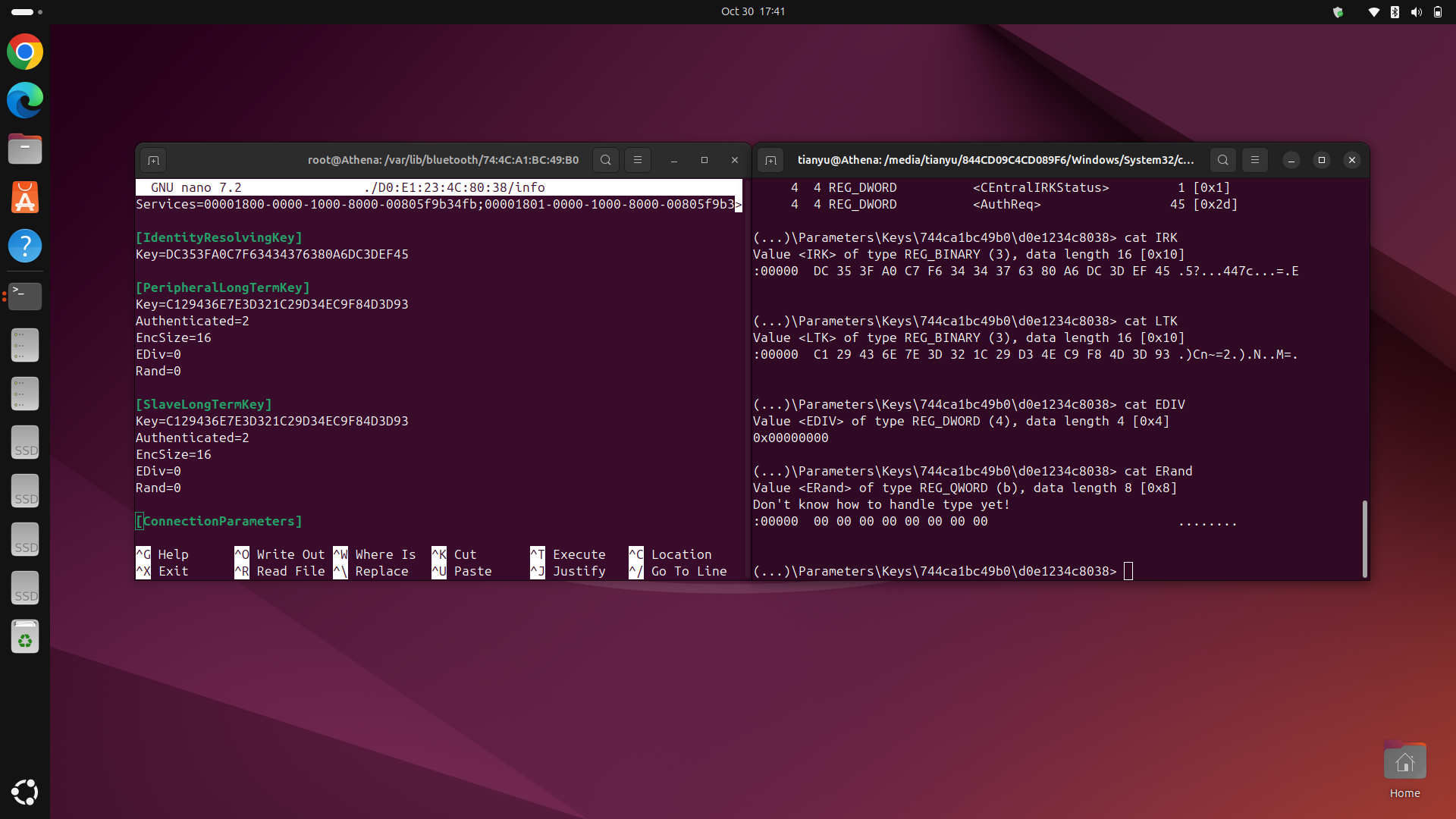
4. In the second terminal, navigate to the Bluetooth configuration directory for Windows:
cd /media/<your-ubuntu-username>/<your-windows-partition>/Windows/System32/config
chntpw -e SYSTEM
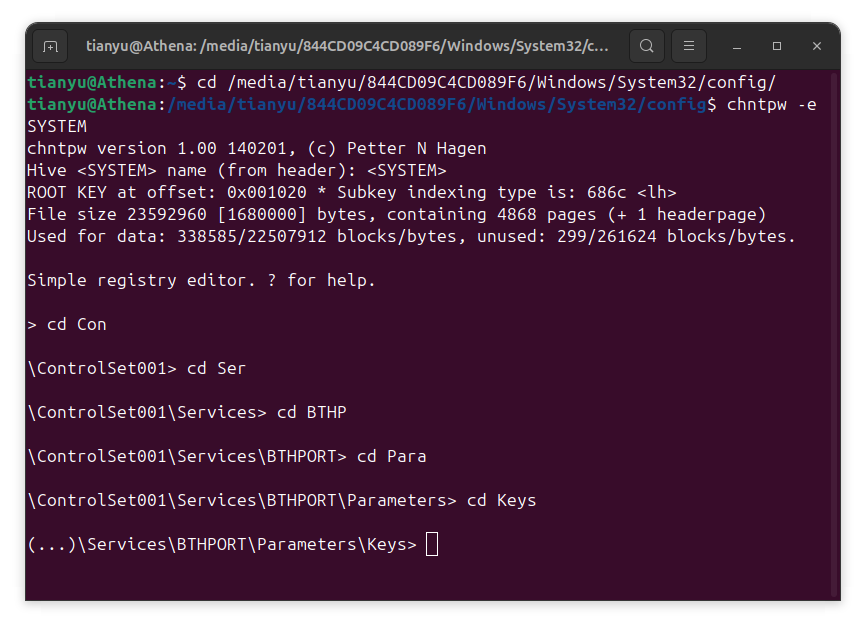
cd ControlSet001/Services/BTHPORT/Parameters/Keys/<your-windows-bluetooth-controller-mac-address>/<your-device-mac-address>/
5. Copy the corresponding key values from Windows to Ubuntu:
- In Windows, use command
cat IRKto look for the keys:IRK,LTK,EDIV, andERand. - Attention: The byte order of
ERandhas to be inverted and then converted to a decimal value. For example, ifERandis88 79 6A 5B 4C 3D 2E 1F, it should be converted to1F2E3D4C5B6A7988in hex, which is2246800662264969608in decimal. Then use this decimal value in Ubuntu. - In Ubuntu, open the
infofile in nano and locate the corresponding fields. Replace the values in Ubuntu with those from Windows.
6. Save the changes in the info file in Ubuntu and exit nano.
7. Restart the Bluetooth service in Ubuntu:
sudo systemctl restart bluetooth
Note on Classic Bluetooth (BR/EDR) Devices
The steps above are for BLE devices. For classic Bluetooth devices (BR/EDR), the process is simpler. You only need to copy the LinkKey value from Windows to Ubuntu.
After completing these steps, the Bluetooth device should be able to connect automatically when switching between Windows and Ubuntu in a dual-boot system.
Q&A
- What if there are multiple Bluetooth devices?
- In Ubuntu terminal, check the
infofile for each device. The file includes the device name. An example entry looks like this:[General] Name=MX Anywhere 3s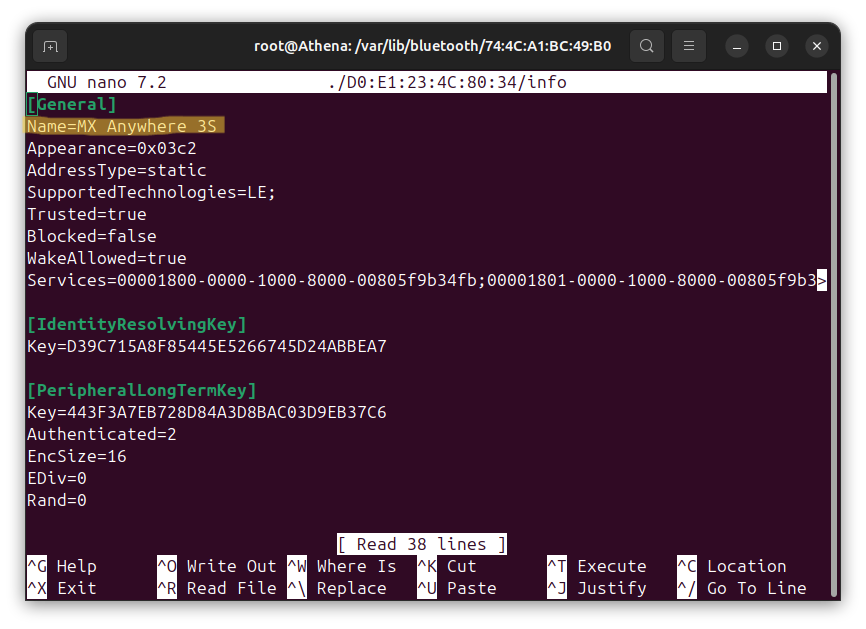
- In Ubuntu terminal, check the
- What if the device still doesn’t connect?
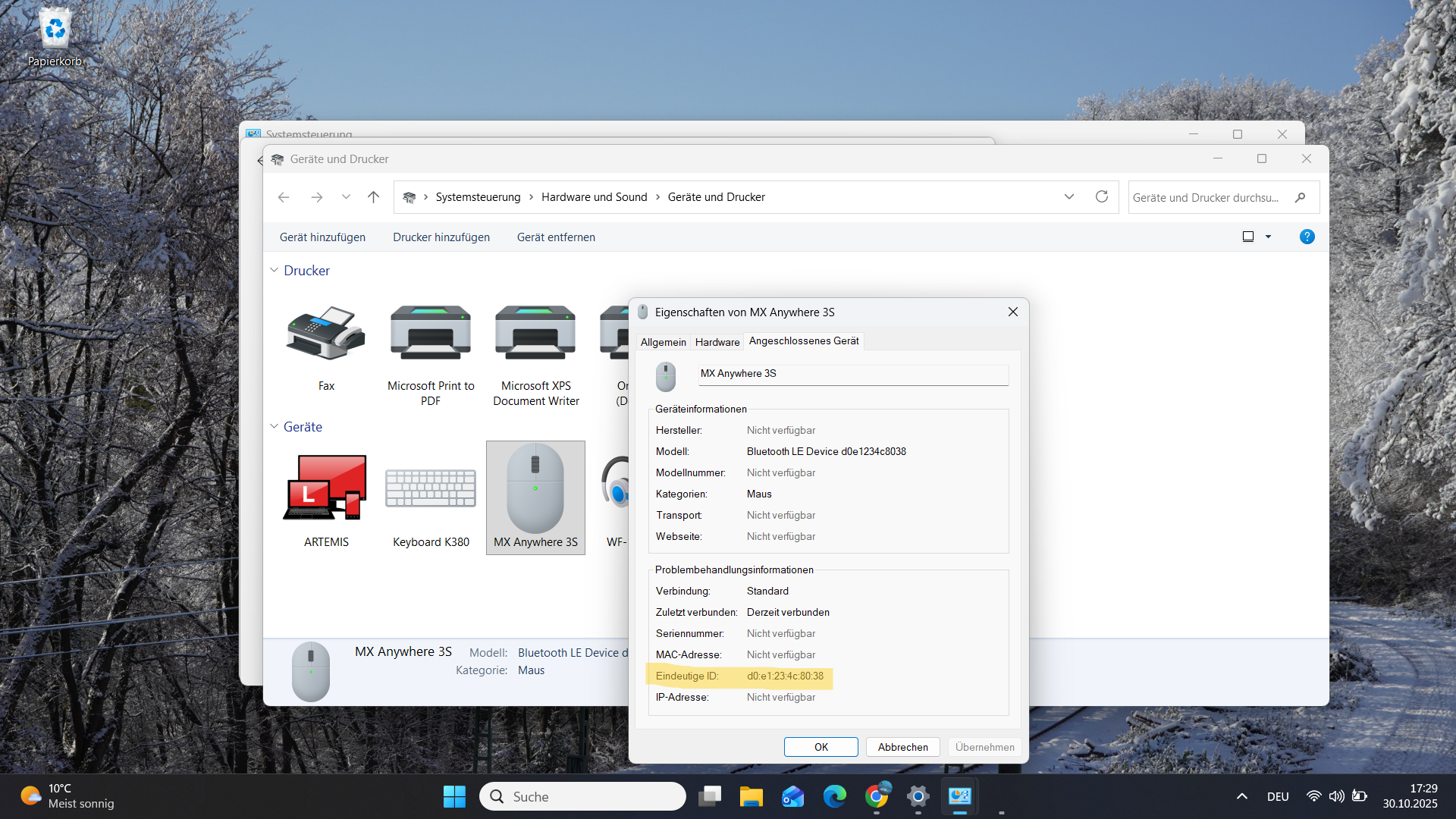
- Ensure the keys are copied correctly and the byte order for
ERandis inverted properly and converted to decimal. Double-check the MAC addresses to ensure they match. - The device MAC address should be the same in both OSes. If they differ, rename the folder in Ubuntu to match the Windows MAC address.
- Step 3 shows how to rename the folder in Ubuntu.
- Ensure the keys are copied correctly and the byte order for

